Antibiotic Resistance – Bells Are Tolling!
 Antibiotics have been available for about 80 years and are prescribed by those practicing conventional medicine to fight off bacterial infections.
Antibiotics have been available for about 80 years and are prescribed by those practicing conventional medicine to fight off bacterial infections.
Simplistically they work by blocking the bacterial processes or preventing the bacteria from multiplying.
It is this brief pause in the lifecycle that allows the body’s immune system to fight the infection.
Today antibiotics, one of the mainstays of orthodox prescribing, are now losing their power and efficacy in a dramatic and frightening way that have massive implications for our global health.
Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance occurs and develops when bacteria that causes illness becomes resistant to previously effective antibiotic medications. Most infection- causing bacteria can become resistant to some antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance is developing at an alarming rate!
After several years monitoring by the World Health Organisation (WHO), antibiotic resistance has been recognised as a public health problem with the WHO now calling it one of the biggest threats to human health today.
In 2013 Australia formed the Antimicrobial Resistance Standing Committee (AMRSC) to oversee antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic use in Australia.
The biggest antibiotic resistant threat to public health today include infections such as Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA or Golden Staph), Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE), and multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Tuberculosis).
Those bacteria that are resistant to several types of antibiotics are called multi-resistant organisms or ‘Superbugs’. Some strains of E.coli associated with some urinary tract infections have become resistant to several types of antibiotic due to being overly misused for this condition.
Bacterial Mutants
Just as viruses such as those that cause colds and flu mutate regularly to avoid being killed, bacteria can also become resistant by mutating their genes after coming into contact with an antibiotic.
Simply put the bacteria change to protect themselves from destruction via the antibiotic. Bacteria can also mutate when it comes into contact with other like strains by passing their genes onto the other bacteria and forming a new antibiotic resistant bacterial strain.
Bacterial mutation is an expected occurrence as the bacteria strive for survival but it is the increase in antibiotic resistance that is the major cause for alarm.
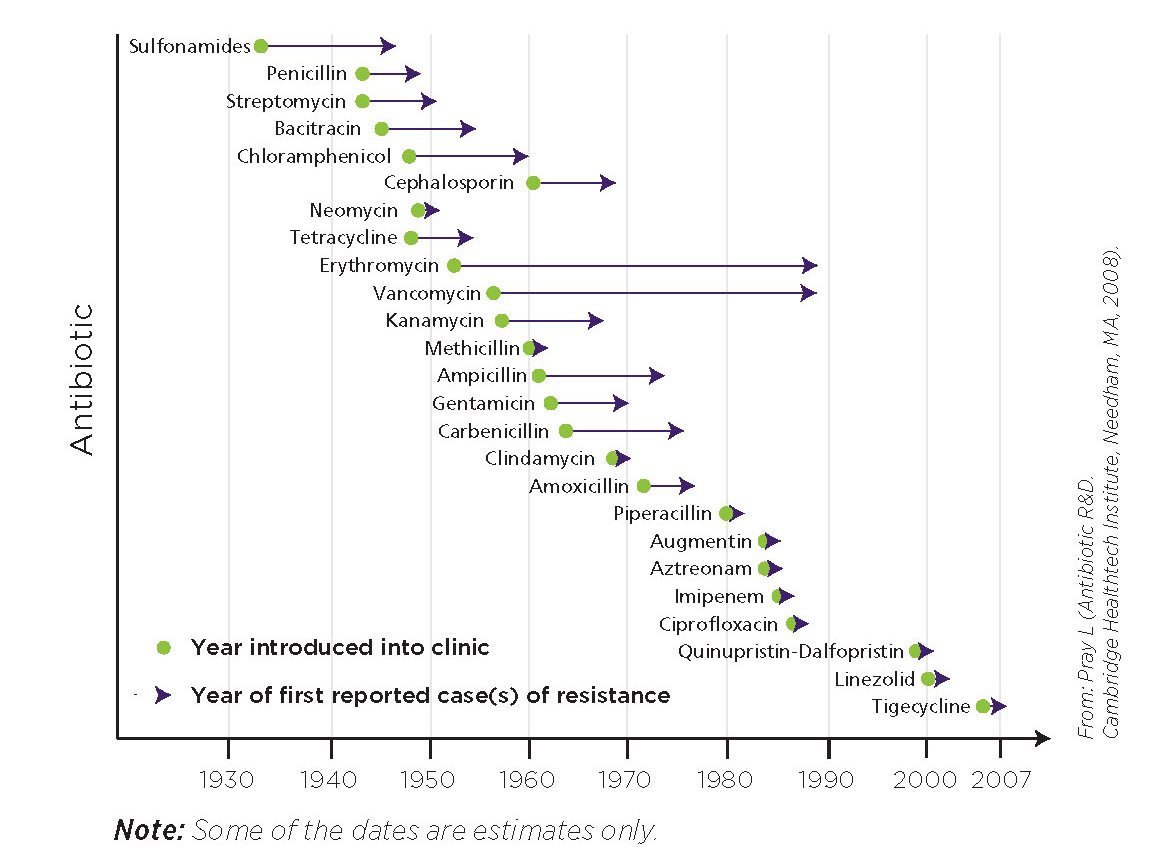
The diagram below depicts the time between the introduction of an antibiotic and the first appearance of resistance and shows just how quickly antibiotic resistance has developed, especially in newer antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance is on the rise due to overuse and abuse of antibiotics.
The overuse of antibiotics in our food livestock is a definitely a contributor but more-so Australia is amongst the highest users of antibiotics in the world with around 22 million prescriptions written every year in primary care.
All too often antibiotics are being prescribed and taken inappropriately and unnecessarily. Upper respiratory infections such as cold and flu, ear infections, skin conditions such as acne, and cystitis are all common examples.
Antibiotics have absolutely no effect in treating viruses, fungal infection or other illnesses that are not related to bacterial infection.
Different types of antibiotics will treat different types and sites of bacterial infection. For example; benzyl penicillin has very little if any effect on gastro-intestinal organisms.
There are broad spectrum antibiotics such as amoxycillin and gentamicin that are effective against a wide range of bacterial infection and narrow spectrum antibiotics such as penicillin that affect only a few types of bacteria.
If You Have to Take a Course of Antibiotics
If you must take antibiotics follow these precautions to limit the growth of progression resistance.
- Take antibiotics at the correctly prescribed time of day
- Take the entire course of antibiotics
- Don’t save unused antibiotics for another time
- Do not share antibiotics with others
- Practice good hygiene and infection control
The reality is that if you get an antibiotic resistant infection it is likely the infection will be more persistent, last for longer and present with complications.
Consequently being infectious for longer has the potential of passing the antibiotic resistant infection on to others thereby increasing the problem.
What GP’s Can Do
With antibiotic resistance being recognised as a public health issue, GP’s have been given the directive to follow the antibiotic creed ‘MINDME’ to avoid inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic prescription.
- Microbiology guides therapy wherever possible
- Indications should be evidence based
- Narrowest spectrum required
- Dosage appropriate to the site and type of infection
- Minimise duration of therapy
- Ensure monotherapy in most situations
The Future
Scientists are already working hard; conducting intensive research to address and combat antibiotic resistance. One study seeks to reverse resistance by determining the genetic steps bacteria go through so that scientists can then reverse this mutation pathway making bacteria once again responsive to antibiotic treatment.
Other research has discovered a way to alter bacteria DNA using phages and mutated viruses making them more susceptible to the antibiotic treatment.
We shall see!
Emed’s comment:
For years Natural Health Practitioners have been cringing at the over-use of antibiotics and the consequential health problems faced by many individuals. Antibiotic use can have an enormously detrimental effect on immune function.
Helping people to build their immune system is one of the therapeutic protocols that Naturopaths do best.
On a positive note, the awareness raised by antibiotic resistance becoming a public health issue appears to have caused the medical profession to take steps toward a more conservative and responsible approach in their antibiotic prescribing. The public awareness campaign helps individuals to take responsibility for themselves to become educated about antibiotics and ask questions when these are prescribed.
Ask yourself if you really need to be taking antibiotics? In some instances certainly they have validity but in many circumstances improving your immune system function is a far healthier option. You can read more about the dangers involved with taking antibiotics in A Prescription for Problems: The Dangers of Antibiotics.
Help yourself to fight off infection. Contact Emed today for a Free Initial Consultation where our Naturopaths can put you on the path to continued good health.
Further reading
- A Prescription for Problems: The Dangers of Antibiotics
- Probiotics for Immune Balance
- Strengthening Your Child’s Immune System
- Probiotics – Exploring Species and Strains
- Colds & Flu
- Garlic Fights Food Poisoning Better Thank Anti-Biotics
- Are Antibiotics Linked to Peanut Allergies?